The Brain Performance Index
The
Brain Performance Index (BPI) is an estimate of the efficiency of neural
resource allocation and it is not designed to replace a neuropsychological test
but rather to compliment neuropsychological evaluations especially where a
patient has problems taking a conventional neuropsychological test or when one
wants to rapidly repeat the test. The Weschler Intelligence test (i.e.,
mazes, coding, block design, digit span, picture completion, math, vocabulary,
verbal I.Q., performance I.Q., full scale I.Q) and the EEG was recorded from 19
channels with a linked ears reference in the eyes closed condition from 339
normal control subjects, age 6 to 18 years of age. EEG
variables that correlated at P < .01 were entered into a multivariate
regression analysis called the Brain Performance Index (BPI) in which
individual neuropsychological sub-tests were the dependent variable and EEG
Phase delays, EEG coherence, EEG amplitude asymmetry and EEG power were the
independent variables. The multivariate regression equations,
referred to as the Predicted Neuropsychological Score (PNS) also computes
the + and – 95% confidence band as a EEG prediction of performance on each
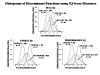
neuropsychological test. The correlation to I.Q. was
approximately 0.58 and involved short time delays between the frontal lobes and
the rest of the brain (faster resource allocation, elevated power (more energy)
and lower coherence (high complexity). These three combined measures
give rise to an overall prediction of the efficiency of neural resource
allocation.
Click here for more details about the Brain Performance Index


Click
here for links to Localization of Function and the NeuroImaging Literature
Click
here for links between Behavior and Brodmann Areas
Click
here for a Map of Functions and Brain Structure
Contact us for more info
|
